Project Structure
Overview
This page provides a detailed overview of the two main repositories at the heart of the unified LimeSDR gateware project:
LimeSDR_GW – the primary LiteX-based SoC framework, covering board/platform/target definitions, SoC integration, bitstream generation, and firmware compilation.
LimeDFB – the modular VHDL-focused signal processing library (Data Flow Blocks), designed for reusability and integration with LiteX via the LimeDFB_LiteX wrapper layer.
The structure is designed to promote modularity, reusability, and portability across diverse FPGA architectures and SDR boards. By leveraging LiteX’s Python-based SoC builder toolkit, the project automates complex hardware integration tasks (e.g., bus connections, clock management, CPU and firmware support), allowing a focus on RF-specific functionalities. LimeDFB complements this by providing modular VHDL components for RF data processing, ensuring a clear separation of concerns: LiteX handles SoC assembly and vendor-neutral abstractions, LimeSDR_GW unifies board-specific configurations, and LimeDFB manages reusable RF logic.
This organization replaces isolated, board-specific HDL projects with a consolidated, sustainable ecosystem. It simplifies maintenance by sharing components (e.g., streaming engines, LMS7002M controllers) across boards, enables easy expansion for new variants without logic duplication, and supports migration to different FPGA families. For a high-level project overview, refer to the Introduction page. When preparing to add or modify boards, fork/clone the repository and use existing platform/target files as templates (e.g., copy from LimeSDR Mini V2 for similar setups). For details on extending the project (e.g., adding boards or features), see Adding a New Board.
LimeSDR_GW Repository Layout
The LimeSDR_GW repository (hosted on GitHub at myriadrf/LimeSDR_GW) is built around the LiteX design flow and includes the following core components:
/ (root)
├── boards/
│ ├── platforms/ <-- Board-specific I/O constraints and configuration files (e.g., pin assignments, timing constraints, FPGA device definitions, programming setups).
│ └── targets/ <-- Integration scripts that define the build process (instantiating LiteX cores, peripherals, CPU, and firmware). These act as the "top-level" for SoC wiring and flow control, including clock/reset domains, memory layouts, and optional features like debugging.
├── docs/ <-- Documentation (design descriptions, build instructions, modification guidelines, etc.).
├── firmware/ <-- Firmware source code for the softcore CPU (drivers and application-specific logic).
├── gateware/ <-- FPGA hardware description files (Verilog/VHDL/LiteX) for custom logic and interconnects, including wrappers for integrating LimeDFB modules.
├── riscv_jtag_tunneled.tcl <-- TCL script for automating JTAG debugging.
├── README.md <-- Project overview and documentation links.
└── .gitignore <-- Files and directories ignored by version control.
Key directories include:
boards/platforms/Physical hardware board definitions (with I/O assignments and constraints). Each board (e.g., limesdr_mini_v2_platform.py) defines a Platform that combines IOs with timing constraints. LiteX uses this to automatically generate toolchain-specific constraint files (for Vivado, Quartus, Diamond, and others).boards/targets/Main SoC entry points (e.g., limesdr_mini_v2.py), which instantiate a board-customized LimeTop SoC. This acts as the central point for CPU integration, peripheral connections, and combining LiteX with DFB modules.gateware/Contains LiteX integration logic and wrappers for external HDL. Notable items include:LimeTop.py– core SoC managementLimeDFB/– submodule or link to the LimeDFB repository (with raw VHDL)LimeDFB_LiteX/– LiteX-compatible VHDL wrappers for DFB modulesexamples/fft/– simple examples (e.g., FFT-based loopback tests)constraints/– additional static timing constraints (e.g., .sdc files)
firmware/C-based firmware for RISC-V softcores (e.g., VexRiscv, PicoRV32). Includes:main.c, peripheral drivers, and build setup (Makefile)
Standard interfaces (for I2C, SPIFlash, LMS7002M configuration, etc.)
Shared across all boards and CPU types
bitstream/Pre-built FPGA bitstreams for supported boards, created through LiteX’s toolchain abstraction.tools/GNU Radio Companion (GRC) and Python scripts for validation (e.g., testing TX/RX paths on Mini V2 or XTRX boards).docs/Sphinx-based documentation, with board-specific build instructions and diagrams.
LimeDFB Repository Layout
The LimeDFB repository (hosted on GitHub at myriadrf/LimeDFB) contains reusable VHDL signal processing blocks, organized by function and supported by detailed documentation. For full details, see LimeDFB documentation. It is designed for reusability and integration with LiteX via the LimeDFB_LiteX wrapper layer.
/ (root)
├── axis/ <-- Shared utilities (e.g., AXI-Stream converters).
├── axis_fifo/ <-- FIFO buffers for data streams.
├── cdc/ <-- Clock domain crossing modules.
├── docs/ <-- Architecture overviews, WaveDrom waveforms, and in-depth module explanations.
├── gt_channel/ <-- Gigabit transceiver channel modules.
├── lms7002/ <-- LMS7002M transceiver controllers.
├── rx_path_top/ <-- Receive path top modules.
├── tx_path_top/ <-- Transmit path top modules.
├── README.md <-- Repository overview and links.
└── .gitignore <-- Files ignored by version control.
Key directories include:
rx_path_top/,tx_path_top/,lms7002/,gt_channel/Specific signal paths and controllers, each with src/ for code, testbenches for verification, and block diagrams for clarity.docs/Architecture overviews, WaveDrom waveforms, and in-depth module explanations.axis/,axis_fifo/,cdc/Shared utilities (e.g., clock domain crossing, FIFO buffers, AXIS converters).LimeTop wrappersintx_path_top.py,rx_path_top.py, etc. These wrap DFB logic as LiteX modules, reused in LimeSDR_GW/gateware/LimeDFB_LiteX.
Integration Between Repos
LiteX manages the build process and incorporates LimeDFB modules through the LimeDFB_LiteX wrapper layer. This separation keeps DSP logic vendor-neutral and purely VHDL-based, while allowing smooth interaction with LiteX’s Python-driven SoC and firmware environment.
Examples include:
The LimeTop SoC instantiates RxPathTop, TxPathTop, and LMS7002Top from LimeDFB_LiteX.
Firmware uses a consistent memory map to access DFB control and status registers.
The same logic can be synthesized for Intel (via Quartus), Xilinx (via Vivado), or Lattice (via Diamond/Yosys) without changes to the VHDL or Python code.
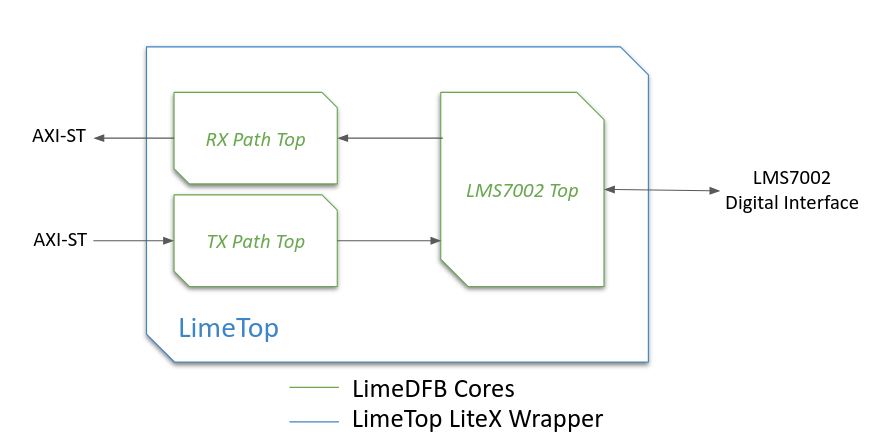
The LimeTop block diagram illustrates the integration of LimeDFB cores (in green) with LiteX wrappes (in blue). AXI-Stream interfaces connect the RX and TX Path Top blocks to the LMS7002 Top, which interfaces with the LMS7002 digital interface. This modular setup allows RF data processing in LimeDFB while LiteX handles SoC-level connectivity and control.
Additional Files
- riscv_jtag_tunneled.tcl (in LimeSDR_GW)
A TCL script used for automating JTAG debugging with the RISC-V softcore. It streamlines tasks such as setting breakpoints and managing JTAG connections.
- README.md (in both repositories)
Provides an introduction to the project, build instructions, and links to additional documentation.
- .gitignore (in both repositories)
Lists files and directories that should be ignored by version control (e.g., temporary files and build outputs).